Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkage. The disaccharide maltose contains two D-glucose residues joined by a glycosidic linkage, which is a covalent bond formed by joining of –OH group of one monosaccharide with the anomeric carbon of the other sugar unit.
Disaccharides can be hydrolysed to yield their constituent monosaccharides by boiling with dilute acid. Hydrolysis of sucrose yields a mixture of glucose and fructose
Conventionally, oligosaccharides are carbohydrates having two to ten units of monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bond. Some commonly occurring oligosaccharides are maltose, lactose, sucrose, etc.
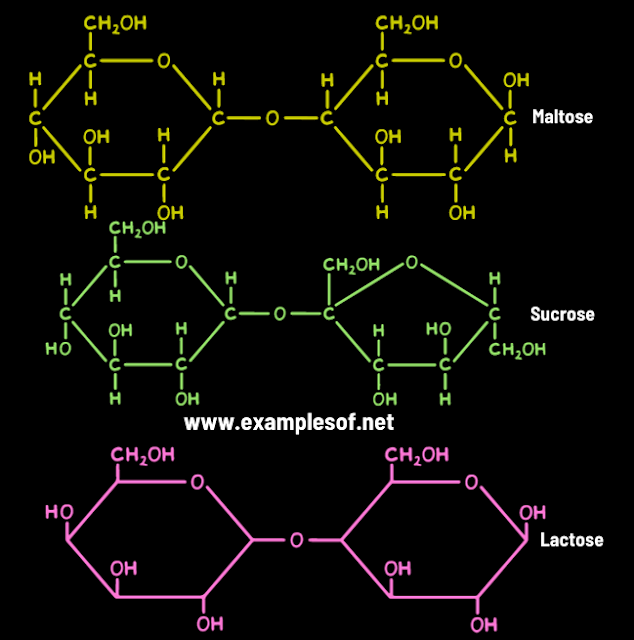
- Maltose,
Sucrose and lactose are biologically
important disaccharides.
- Maltose: It is called malt sugar. It is produced during the
germination of starchy seeds. Two glucose molecules are joined to
form a molecule of maltose.
- Sucrose: It is common cane sugar or table sugar. It is formed by the union of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. It is a storage product of photosynthesis in sugar cane and sugar beet. It is the sweetest among naturally occurring sugars.
- Lactose: It is called milk sugar. It is made up of D-galactose and D-glucose residues.