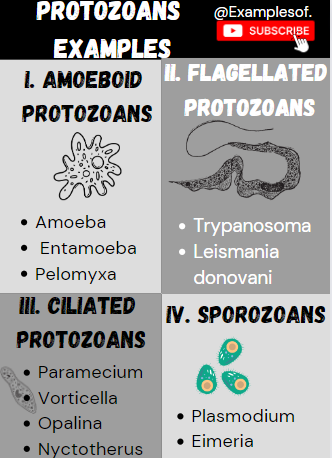
All protozoans are heterotrophs and live as predators or
parasites. They are believed to be primitive relatives of animals. There are
four major groups of protozoans.
- Amoeba
- Entamoeba
- Pelomyxa
II. Flagellated
protozoans: The members of this group are either free-living or parasitic. They
have flagella. The parasitic forms cause diseases such as sleeping sickness.
Examples of Flagellated protozoans:
- Trypanosoma
- Leishmania donovani
III. Ciliated protozoans: These are aquatic, actively moving
organisms because of the presence of thousands of cilia. They have a cavity
(gullet) that opens to the outside of the cell surface. The coordinated
movement of rows of cilia causes the water laden with food to be steered into
the gullet.
Examples of Ciliated protozoans:
- Paramecium
- Vorticella
- Opalina
- Nyctotherus
IV. Sporozoans (Parasitic
protozoans): This includes diverse organisms that have an infectious
spore-like stage in their life cycle. The most notorious is Plasmodium
(malarial parasite) which causes malaria, a disease which has a staggering
effect on human population
Examples of Sporozoans:
- Plasmodium
- Eimeria